Market equilibrium
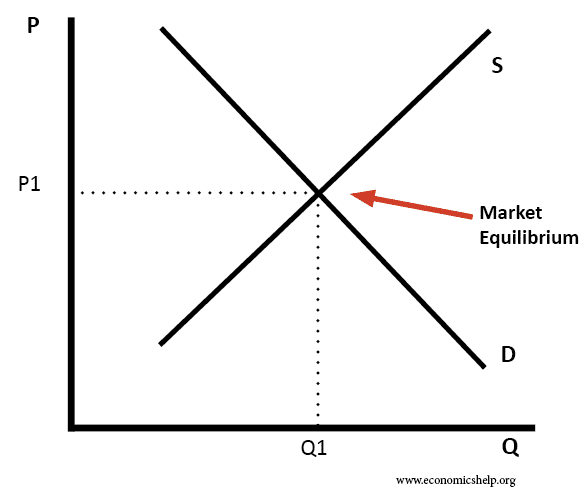
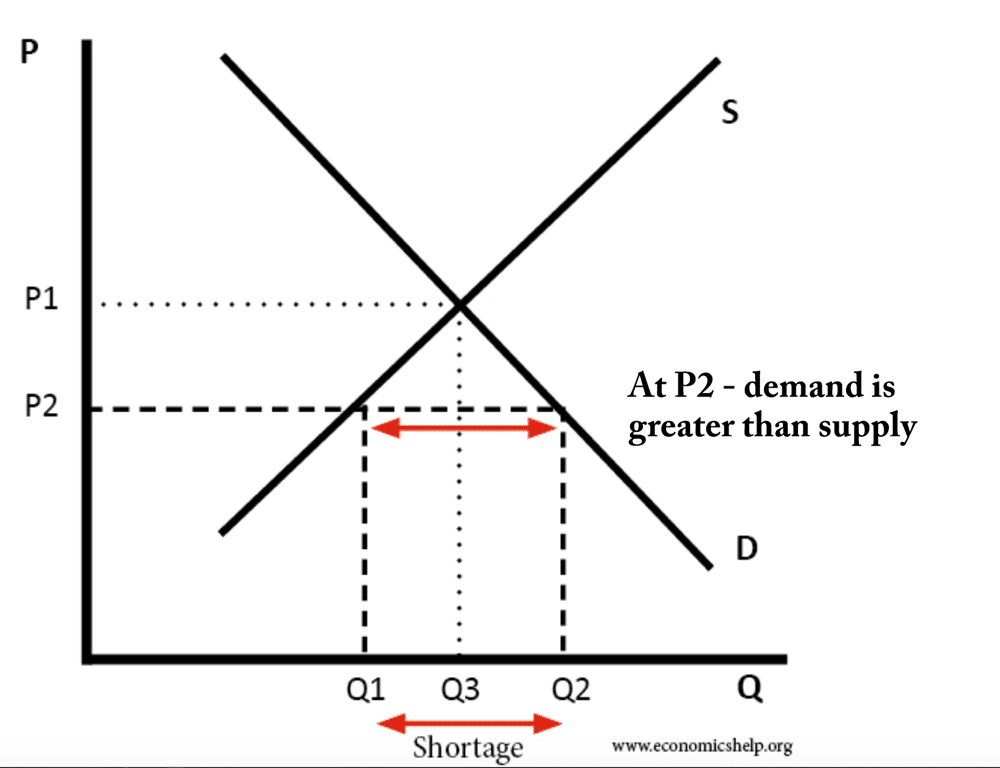
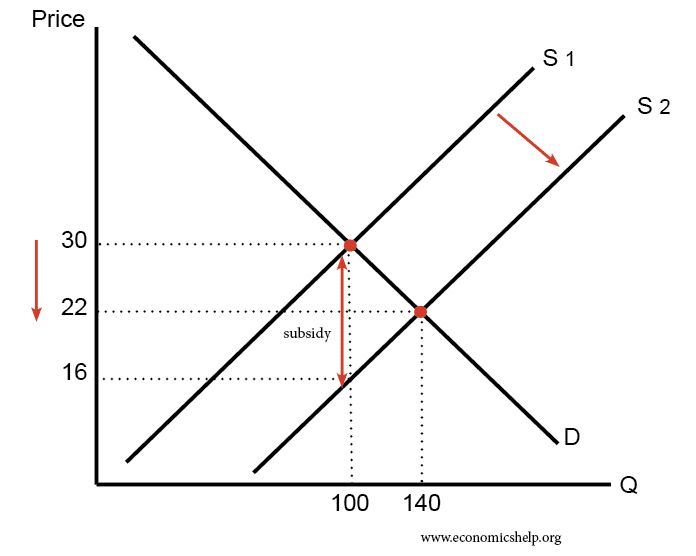
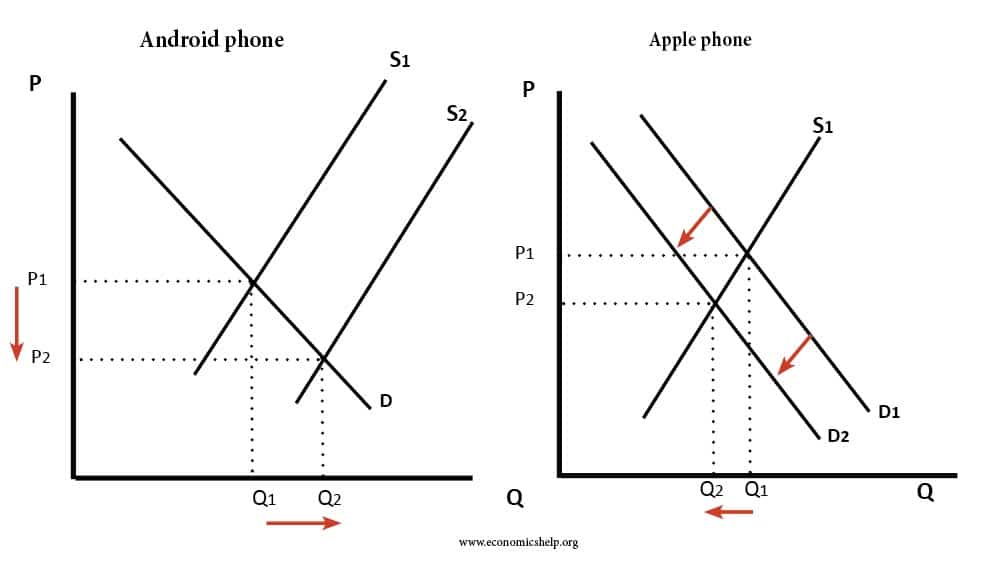
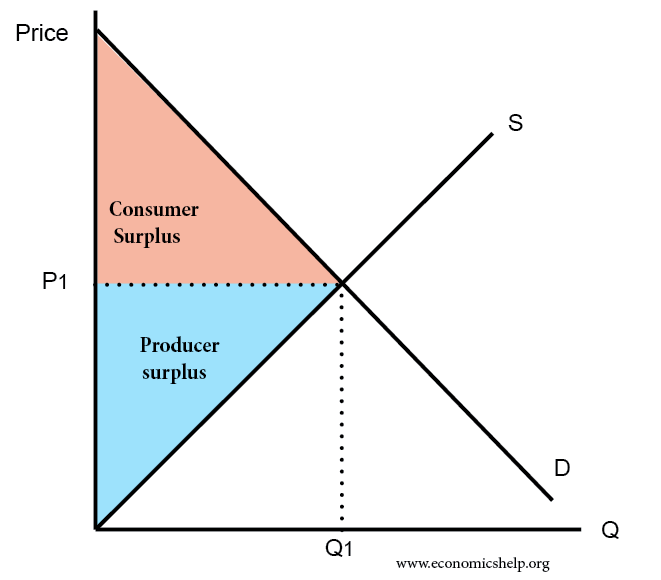
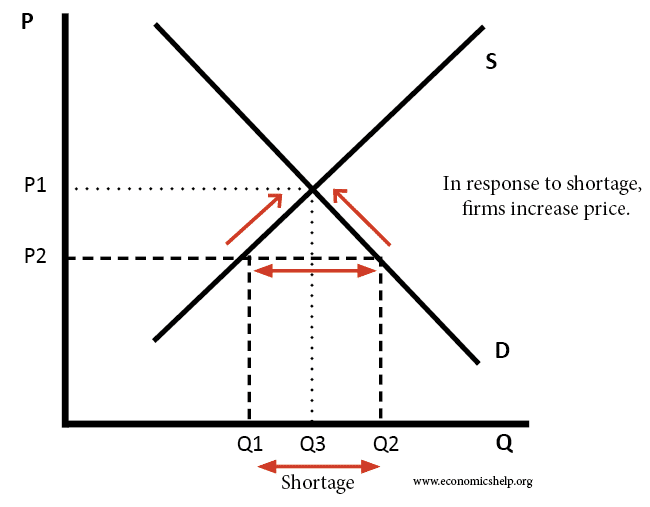
Definition of market equilibrium – A situation where for a particular good supply = demand. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. We say the market-clearing price has been achieved. A market occurs where buyers and sellers meet to exchange money for goods. The price mechanism refers to …